Cache Memory
Definition
What is cache memory?
Cache memory is a chip-based computer component.
It can make the data be retrieved from the computers memory more efficiently.
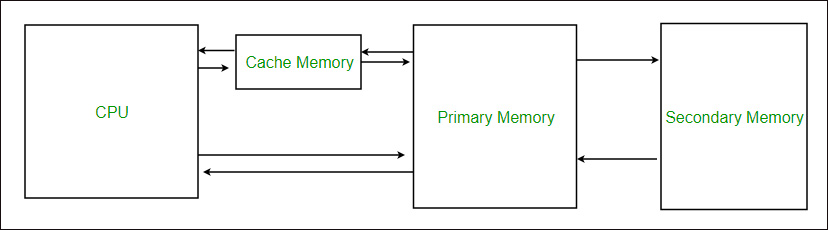
What is the purpose of cache memory?
It can be used to speed up and synchronize with high-speed CPU.
It saves frequently requested data and instructions so that they can be used to CPU immediately when needed.
Cache memory is more expensive than main memory or disk memory, but less expensive than CPU registers.
It is usually embedded as a CPU cache in the processor chip.
Level 2:Level 2 cache is the secondary cache, which is usually larger than level 1 cache.
Now, the trend is to integrate all three levels of memory cache into the CPU itself.
The details are as follow:
Direct mapping:The simplest technique is direct mapping.
It maps each block of main memory to only one possible cache line.
Or, in direct mapping, allocate each memory block to a specific line in the cache.
The address space is divided into two parts: the index field and the label field.
Any block can enter any line of the cache.
This makes it possible to place any word anywhere in the cache.
It is considered as the fastest and most flexible form of mapping.
Set association solves the problem of possible jitter in direct mapping methods.
A block in memory can then be mapped to any row of a particular collection.
Cache memory performance is usually measured in an amount called the hit ratio.
you could use larger cache block sizes, higher associativity, and reduced miss rates.
Improve cache performance by reducing the cost of misses and reducing the time to hit the cache.
You have known the definition, types as well as the propose of it.
Besides, it’s possible for you to also know cache memory performance and mapping from this post.