This post shows you what SSD is.
Do you know whatSSDis?
What Is SSD?
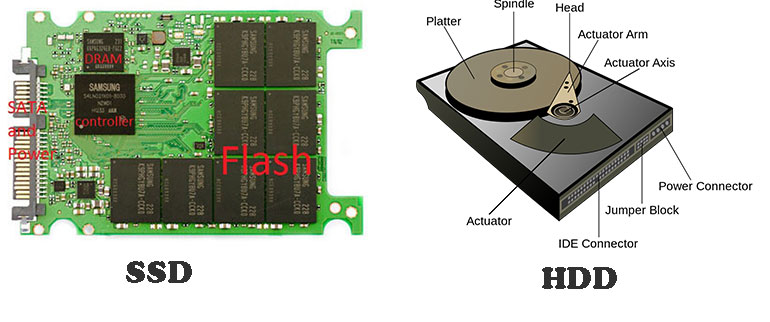
DRAM, short forDynamic random-access memory, features a read-and-write speed faster than NAND flash chip.
However, once powered off, DRAM will lose data.
NAND flashis a non-volatile storage technology, that is, data can still be saved after power failure.
In addition, NAND flash chip can also be divided into plane NAND flash memory, and3D NANDflash memory.
Buffer Chip
The buffer chip stands next to the controller chip.
With it, SSDs can process data faster.
The hard disk interface determines the connection speed between the hard disk and the computer.
In general, SSD has the interface specification same as common hard disk.
For example, it may have interfaces like SATA,mSATA, M.2, and U.2.
These interfaces support AHCI protocol.
However, SSD also has an interface that only supports NVMe protocol, that is, PCIe.
Click3 SSD Terminologies you should probably Know when Buying SSD Driveto know some SSD terminologies.
TheDRAM-based SSDadopts the DRAM as its storage medium.
It is characterized by very fast data access, generally less than 10 microseconds.
Theflash-based SSDmainly adopts non-volatile NAND flash memory.
NVMe SSD indicates that this SSD uses NVMe protocol, which is also related to interface.
To some extent, the interface punch in will affect the data transfer rate of the SSD.
Faster speed.As SSD uses flash memory, reading speed is relatively faster than that of traditional hard disk.
In addition, there is no head in SSD, so seeking time is nearly 0.
No noise.Solid-state drives dont have mechanical motor and fan, so the working noise value is 0 db.
However, most of the SSD can work within -10 to 70 degrees Celsius.
Easy to carry.Compared with the conventional hard disk, SSD is lighter in weight.
Disadvantages of SSD
SSDs also have disadvantages.
Here list some of them.
Flash SSDs have limited write cycles, which is related toSSD lifespan.
In theory, when the write cycles are run out, the SSD is scrapped.
Therefore, in theory, the HDD lifespan is longer than the SSD lifespan.
Capacity.Due to the high cost, the capacity of SSDs is usually less than that of HDDs.
Whats the difference between solid-state drive and hard drive?
Which one to use for your PC?
Read this post to learn more on SSD VS HDD now.
Related Concepts and Technologies
1.
Plane NAND and 3D NAND Technology
At first, SSDs useplane NAND technology.
In this situation,3D NAND technologycomes out.
This technology stacks multiple layers of data storage unit vertically, enabling higher storage capacity in a smaller space.
More stacked layers mean bigger storage capacity.
SLC, MLC, TLC, and QLC
At first, manufacturers usually use SLC.
Thewear levelingalgorithm is integrated into the firmware of the master controller.
This technology ensures data security and SSD performance.
so you can avoid filling the SSD with stale pages, the garbage collection comes out.
When idle pages in the SSD become less than a certain amount,garbage collectionwill be triggered.
Its process is as follows:
(1) Copying the valid data to a reserved block.
(2) Erasing the original block to get a new available block.
The SSD cant identify the deleted data as invalid data until the OS sends aTRIMcommand to the SSD.
TheTRIMcommand makes the SSD know which pages are no longer considered for use and marks them as deleted pages.
Over-provisioning (OP)
Over-provisioningrefers to the capacity that the user cannot operate.
Therefore, OP can reduce write amplification, improve performance and SSD endurance.
Write Amplification (WA)
Flash memory must be erased before it can be written.
In this process, user data and metadata are moved or rewritten more than once.
Many factors will affect the WA of an SSD.
(2) Over-provisioning can reduce write amplification.
The larger the OP, the lower the WA.
(3) Turning on the TRIM instruction can reduce the WA.
(5) Sequential writing can reduce write amplification while random writing will greatly increase write amplification.
(6) Wear leveling will increase write amplification.