Some of these features and advantages are discussed in today’s article.
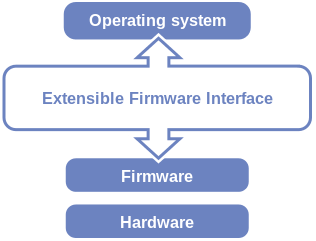
It is seen as the successor to theBIOSand is expected to eventually replace the BIOS.
UEFI does the same thing as BIOS but does it differently.
The ESP partition will also contain the bootloader for the operating system installed on your gear.
This process continues until the operating system is fully booted.
This sounds good; however, this function has a negative impact.
When the first UEFI implementation started shipping, most vendors were not ready for this.
Only a few vendors can sign their operating systems to use secure boot.
Today most UEFIs (though not every UEFI) allow shutdown and secure boot.
This results in a less secure installation but allows booting unsigned operating systems.
As talking about UEFI, the follow-up to BIOS, we cant avoid comparing UEFI to BIOS.
UEFI supports both 32-bit and 64-bit architectures.
Therefore, it can use more RAM to complete a more complicated process than the BIOS.
UEFI also supports CPU independent architecture and drivers.
Unlike BIOS, UEFI has a simpler graphical user interface and supports mouse operations.
Typically, UEFI-enabled computers have faster startup and shutdown time than BIOS-based computers.
Because with computers now booting so fast, you only have very limited time to do it.
you could try this method:
1.
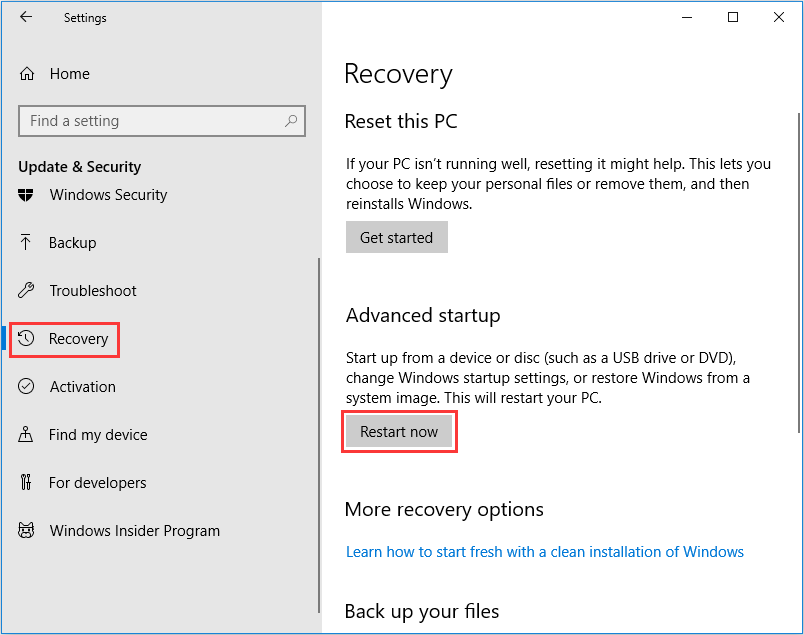
Click theStartand selectSettings, after that, chooseUpdate and Security.
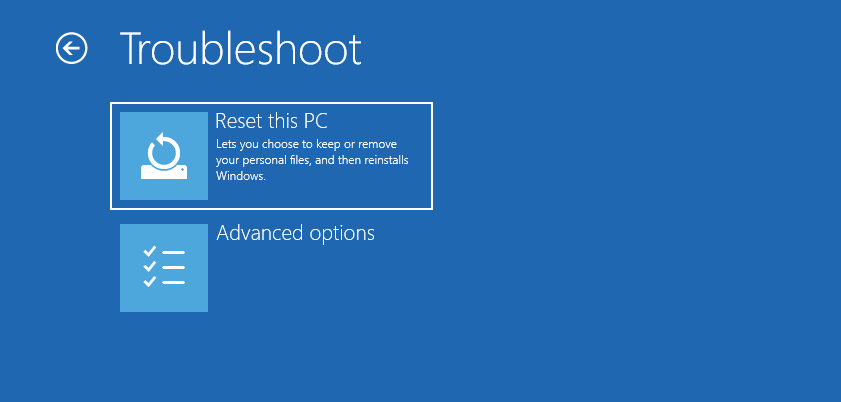
ClickTroubleshoot>ChooseAdvanced options.
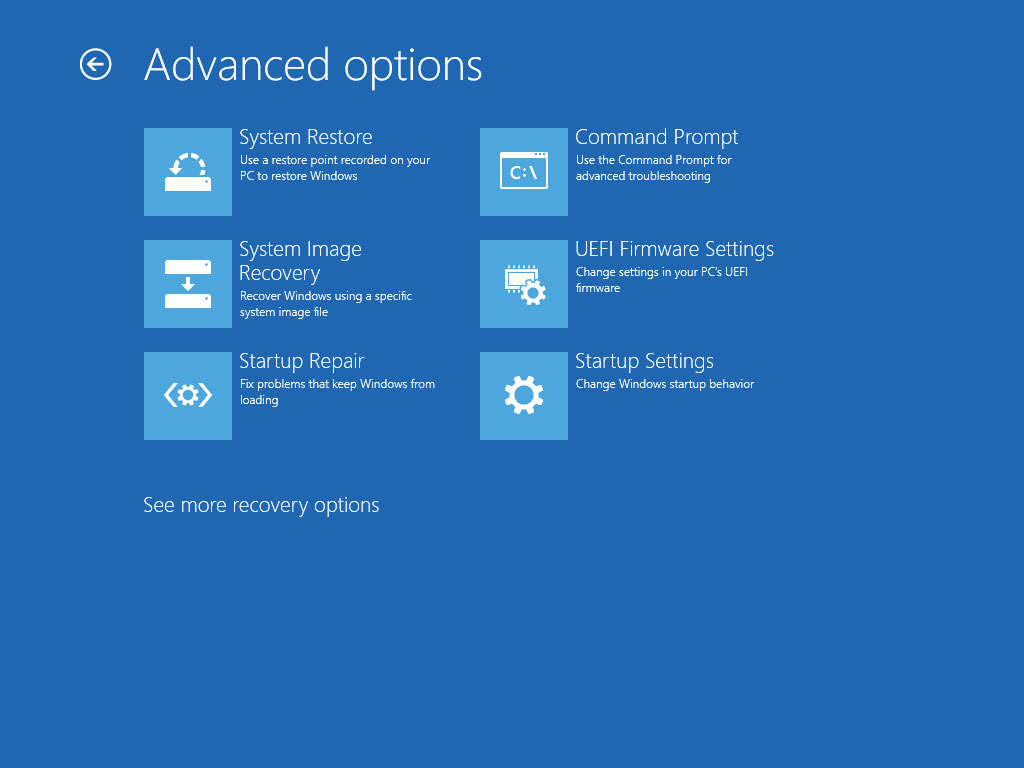
After that, selectUEFI Firmware tweaks.
ClickRestartto restart the system and enter UEFI.