Each approach has advantages and disadvantages in scalability, customization, cost, deployment, and ease of use.
In our previous posts, we have discussedNAS vs DAS,NAS vs Cloud, etc.
Today, we will discuss NAS vs Server.

It connects directly to the Ethernet switch linked to the server.
QNAP vs Synology: which is a better choice for you?
This post will show you a comparison of them and help you to find the answer.
Likewise, an entry-level NAS will be cheaper than an entry-level server with the same amount of storage.
This comes back to flexibility since NAS is really only built to store and access data.
Its this single-purpose design that makes NAS simple.
After purchasing and/or assembling the gadget, the setup process is easy.
They usually just need to be powered up and connected to a data pipe to get started.
However, this is a common trade-off in technology.
They are purpose-built for this role and can be assembled or modified to match the hardware exactly as needed.
This advantage is also the main argument for the connection Attached Server (NAS) alternative.
NAS vs Server: Work Principles
NAS provides cost-effective and easy-to-implement options for increasing storage capacity.
Other devices on the internet use the NAS storage feature.
NAS devices are self-contained devices that typically have at least two bays for inserting storage modules.
The more bays, the more storage space it’s possible for you to achieve.
NAS devices are typically file-based, while server-based devices can be block-based or file-based.
This makes them compatible with most operating systems.
Capacities can range from a few terabytes to tens of terabytes.
Other servers, such as software servers, coexist in the infrastructure.
NAS vs Server: Apps and Pricing
NAS devices can also be used to host applications.
They also offer fewer choices when it comes to the apps users can run.
NAS equipment vendors require users to choose one of their own applications rather than any third-party software.
Differences in functionality between file servers and NAS appliances create cost differences.
File servers provide more processing power, so they are more expensive.
In contrast, most NAS software comes with the NAS machine and does not require a license.
Functionality:Consider the size of your operation and how much you plan to grow in the future.
NAS systems are generally considered suitable for small offices where files are shared between two or three devices.
Scaling up in the future means more purchases and more drives or devices.
NAS devices often limit the security measures you could deploy on their systems.
Shareability:Choose a NAS that allows control of user access, which is important for data security.
As a small business, choosing between a NAS or a server is more speculative.
Redundancy is more important even in non-technical small businesses.
If your business grows, so will your internet needs.
It also depends on what you are selling.
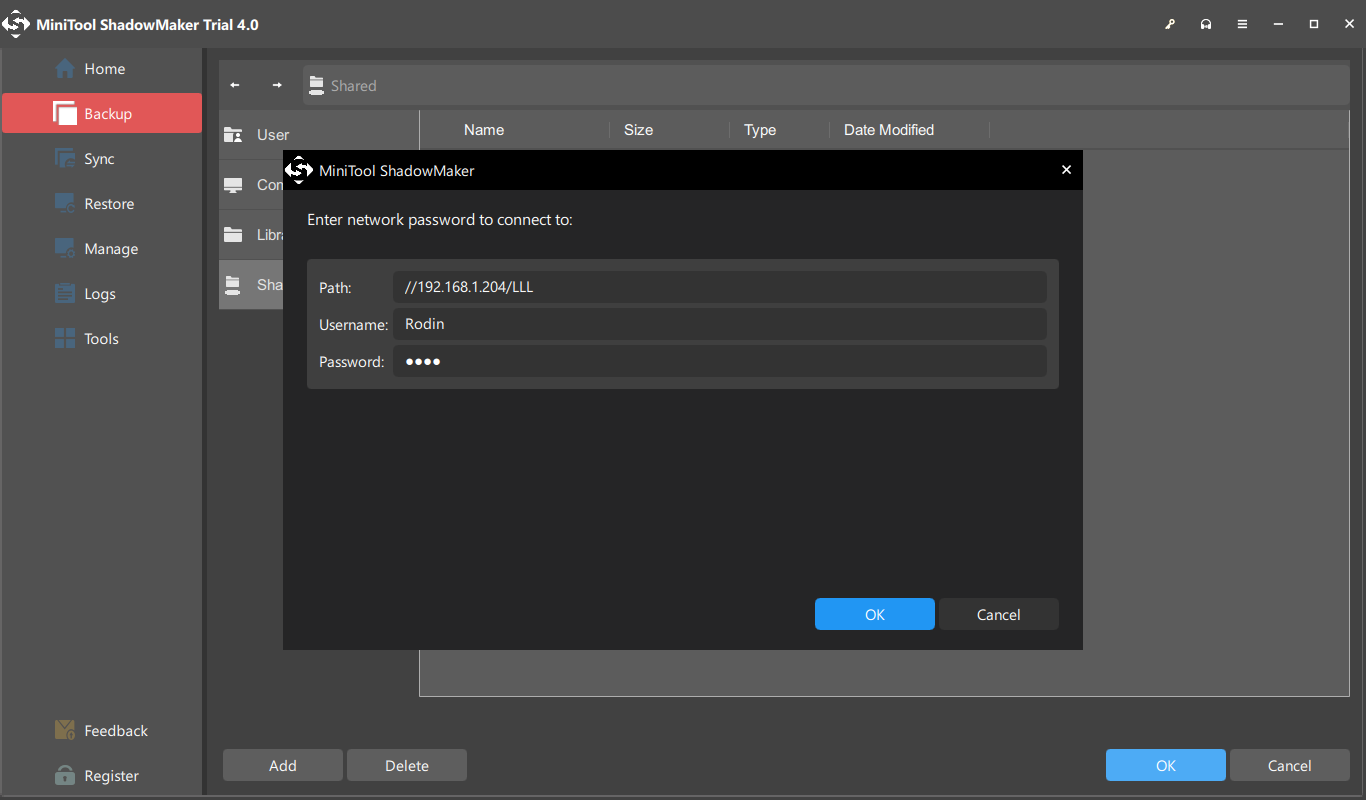
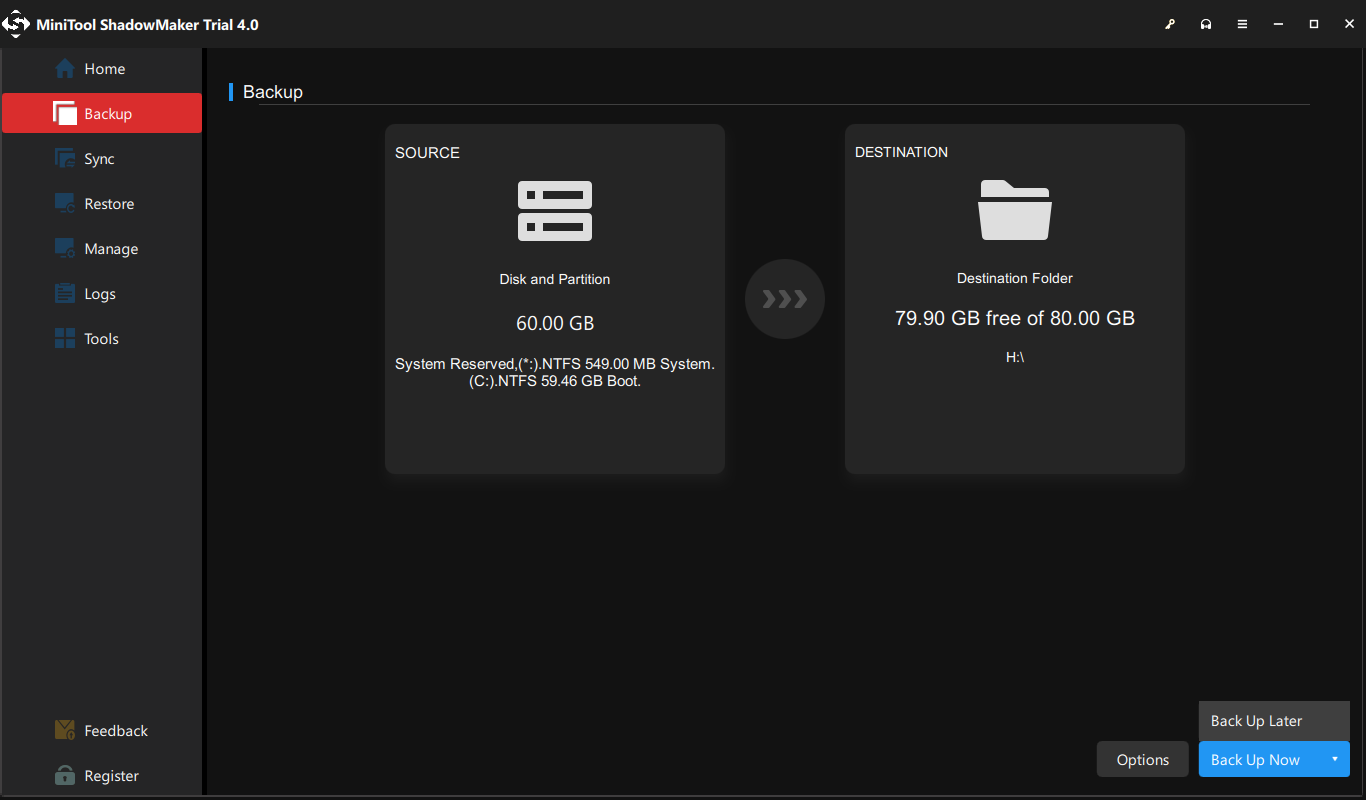
In addition, it is a user-friendly program to protect your setup and data.
And you could restart the delayed backup task in theManagewindow.
Tips
To get more details about MiniTool ShadowMaker controls, refer toBackup controls.
NAS devices enable many computers to share the same backup server at one time.
Bottom Line
To sum up, this post has introduced information about NAS vs Server.