What is RAID 1 and what is RAID 5?
What is the difference between them?
Whats more, you’re free to know how to protect your data.
RAIDis short for Redundant Array of Independent Disks, which is data storage virtualization technology.
It combines plenty of physicaldisk drivecomponents into one or more logical units to achieve data redundancy and/or improve performance.
Different RAID levels require different numbers of hard drives and provide various redundancy, fault tolerance, and performance.
Introduction to RAID 1
Firstly, you should know some basic information about RAID 1.
RAID 1 is composed of data mirroring without parity, striping, or spanning.
Data is written to two or more drives identically, creating a mirrored set of drives.
Therefore, any drive in the set can satisfy any read request.
The actual read throughput achieved by most RAID 1 is slower than the fastest drive.
Write throughput is usually slower because the slowest drive limits write performance.
As long as at least one drive is running, the array will continue to run.
Related post:RAID 5 vs RAID 10: Whats the Difference and Which One Is Better?
If more is needed, other pairs must be added.
That is, x3 2 TB drives = 6 TB 2 TB = 4TB available.
RAID 1configuration is very simple all data is stored identically on several physical disks.
There are often only 2 disks in RAID 1, but more disks can be added for additional redundancy.
RAID 5provides fault tolerance through redundancy.
RAID 5 adopts distributed parity, so parity blocks are stored on each physical disk in a round-robin fashion.
RAID 1
Compared to using only one physical disk, read operations on RAID 1 are faster.
This is because data can be read in parallel.
Therefore, the slowest disk in the array becomes the bottleneck.
RAID 5
Since RAID 5 adopts striping, read operations occur in parallel and are very quick.
RAID 1possesses brilliant fault tolerance.
On condition that one of the physical drives in the array is functioning normally, RAID can function.
RAID 5adopts striping to offer the performance advantages of RAID 1, while also providing fault tolerance.
If a physical disk in RAID 5 fails, the system will maintain the read function.
Due to the overhead of calculating parity, reads and writes during error recovery will be slow.
For example, if one of the RAID 5 hard disks fails, data recovery will be difficult.
Click to Tweet
How to Protect Your Important Data?
Then how to back up your hard drive?
MiniTool ShadowMaker is the top-recommended, which is aprofessional backup tool.
It aims to back up your Windows system, disks, partitions, files, and folders.
Whats more, you might also use it to sync files andclone a hard drive to SSD.
Now follow the instructions below to back up your hard drive to protect your important data.
Step 1: Download and launch MiniTool ShadowMaker.
MiniTool ShadowMaker TrialClick to Download100%Clean & Safe
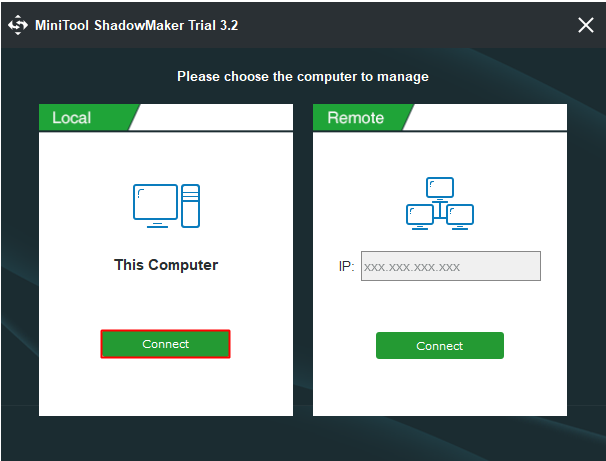
Step 2: ClickConnectinThis Computerto enter its main interface.
Step 3: Go to theBackuppage.
Then clickSourceto choose the backup source.
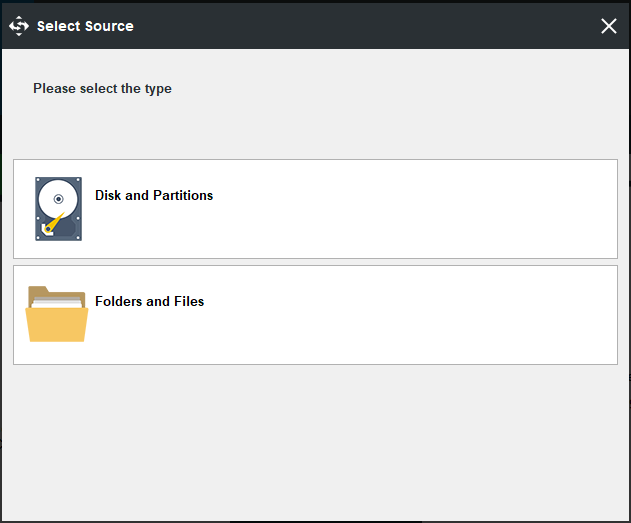
Step 4: ClickDisk and Partitions.
Choose the hard drive that you want to back up, and then clickOK.
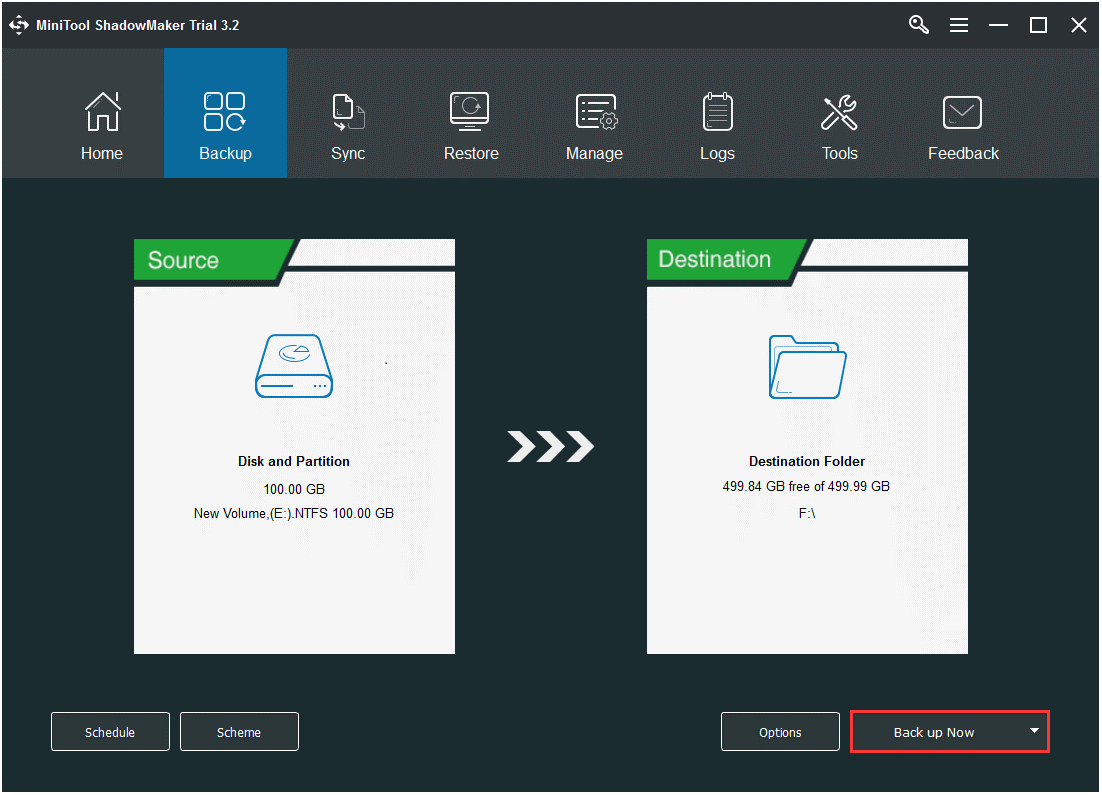
Step 5: ClickDestinationto choose the hard drive to secure your backup image.
better to choose an external hard drive and never nudge the source disk as the target disk.
Step 6: After confirming the backup source and the destination, clickBack up Nowto start the task.
After the process is finished, then you have backed up your hard drive successfully.
So it’s possible for you to use the backup image to restore the hard drive if it fails.