With this technology, users can save different data into different drives.
RAID also provides the Parity Check feature.
Thus, even if the hard disk in the array is damaged, users still can read the data.

The external disk array cabinets are widely used on large servers.
Although this product provides Hot-Swap feature, it is expensive.
Disk array not only provides online expansion feature but also can help to automatically recover data.

In addition, it provides a reliable and available way to manage data.
Merit and Demerit
Merits
RAID helps to increase the transmission rate.
It can simultaneously store and read data from different disks to improve the data throughput of the storage system.
In addition, in RAID, users can make multiple drives transfer data at the same time.
It provides fault tolerance through data validation.
In addition, many RAID modes provide complete cross-check/restore measures to improve the system redundancy effectively.
Demerits
RAID 0 doesnt provide any redundancy.
The disk utilization of RAID 1 can only reach 50%.
RAID 0+1 can provide data safe safeguard.
However, it needs more disk space.
Standard Levels
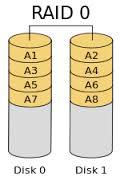
RAID 0
RAID 0 consists of stripping, without mirroring or parity.
It needs two or more hard drives.
Although it can help to increase the performance and throughput of disk, it doesnt provide any redundancy.
However, it costs lowest at all.
To solve this problem, users can createstriped volumeon multiple drives.
Here, it’s possible for you to use MiniTool Partition Wizard tocreate striped volume.
Striped volume can help to distribute data into all drives averagely.
But, users had better not connect all hard rives into a controller.
If users frequently read and write operating system, it is easy to overload the controller.
Aiming at this situation, users can use multiple disk controllers.
RAID 0 provides more free space and better performance, but the whole operating system is very unreliable.
Therefore, if users dont care the data security, they can turn to the RAID 0.
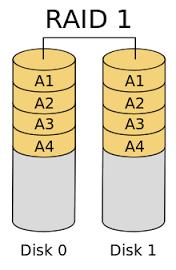
Each drive in a mirror contains an identical copy of the data.
Therefore, when an individual drive fails, the second one can continue to work.
Although RAID 1 can perfectly protect the data security, its disk utilization is 50%.
For example, there are four 80G hard disks, but the available space is 160GB.
In addition, if the hard disk fails, users should timely replace the damaged hard disk.
Otherwise, the rest of the mirrored disk will go wrong, and the whole operating system may collapse.
After replacing hard disk, users can get into the original data as before.
Therefore, the RAID 1 is used to save significant data.
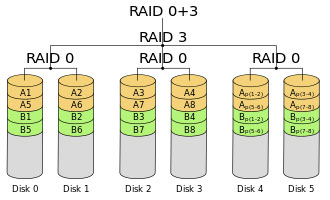
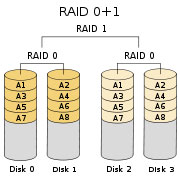
RAID 0+1
RAID 0+1 is a combination of RAID 0 and RAID 1.
It is a RAID level using a mirror of stripes.
Such implementation has the benefits of RAID 0s speed and RAID 1s safety.
RAID 0+1 requires at least 4 hard disks.
LSI Nytro aims to increase speed.
It takes full advantages of the flash technology to improve the data I/O speed.
LSI Syncro is mainly used for data sharing.
It can improve system availability and scalability, and can reduce costs.
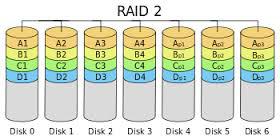
RAID 2
Like RAID 3, data will be stripped and stored in different hard disks.
But RAID2 uses a certain coding technology to check and fix errors.
However, to make use of the Hamming-code, users must pay for data redundancy.
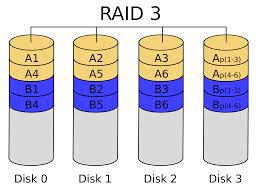
RAID 3
Although RAID 3 can help to check errors, it is unable to fix them.
RAID 3 needs three or more hard disks to store and write data.
It is mainly used for graphics (including animation).
RAID 3 uses a single block of disk to store parity information.
Thus, if a disk fails, the others can be re-generated.
RAID3 can provide a good transfer rate for massive and continuous data.
But for random data, the parity disk will become the bottleneck for operating.
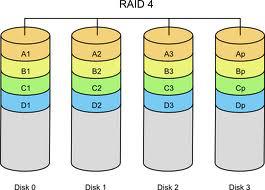
RAID 4
RAID 4 consists of block-level stripping with dedicated parity.
It helps to access data through data block, but its efficiency is not very good.
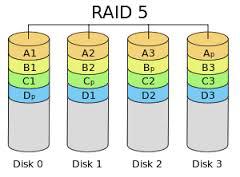
RAID 5
RAID 5 consists of block-level stripping with parity in all disks.
It can help to quickly read and write data.
The parity information is distributed on different disks to improve reliability.
Compared with RAID 3, it just operates one hard disk rather than all disks every time.
Upon failure of a single drive, subsequent reads can be calculated from the distributed parity.
But, the controller design becomes more complex.
Each disk has a cache memory.
Therefore, when multiple users visit the system, the access time is almost close to zero.
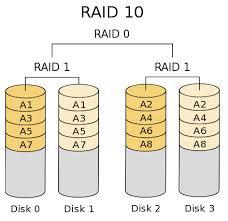
RAID 10
The RAID level 10 contains a strip structure and a mirror structure.
But, its scalability is not very good.
It is suitable for the database which requires speed and error control.
It also contains the same fault tolerance and overhead as RAID 3.
However, it is a very expensive solution and requires all drives have the same synchronization.