Directories organize your documents and other data on your gear well.
It is needed to know whether a file exists before making changes to this file.
Windows PowerShell helps you to navigate, create, and delete files with various command lines.
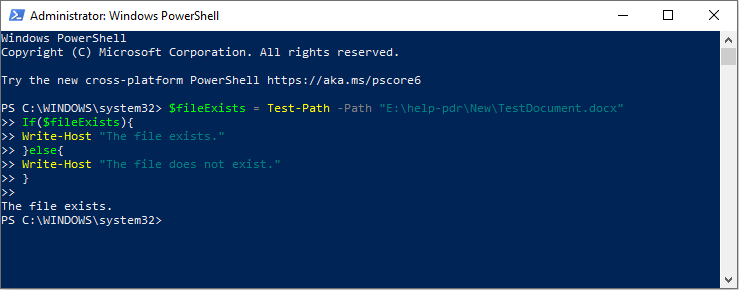
you’re free to try the following command lines to find out if a file exists in PowerShell.
It will give a value to show you the result.
Here are the steps to use the Test-Path syntax.
Step 1: Right-hit theWindows iconbutton and chooseWindows PowerShell (Admin)from the WinX menu.
Step 2: Copy and paste the following command lines and hitEnter.
You should change the path: E:\help-pdr\New\TestDocument.docx to the real path you want to check.
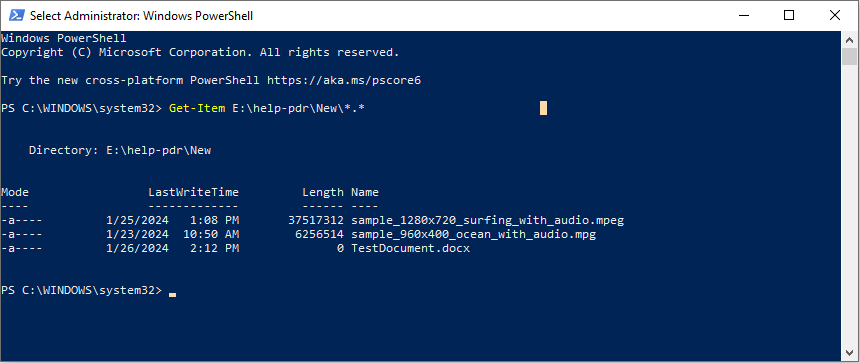
you’ve got the option to learn more about this syntax fromthis page.
To spin up the Get-Item syntax, you better run Windows PowerShell as administrator.
Afterward, copy and paste the following command lines and hitEnter.
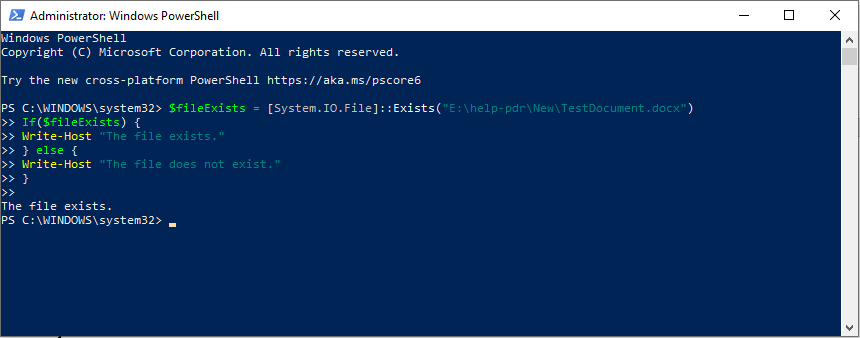
(Replace the file path to the actual file path.)
The File Class allows you to create, copy, move, delete, and open a file.
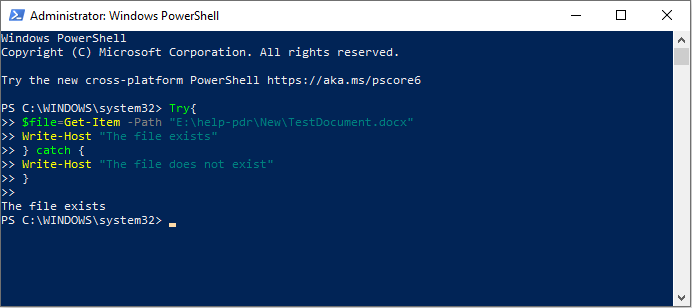
it’s possible for you to also run this syntax to check whether a file exists.
You should open Windows PowerShell and run it as administrator as well.
Copy and paste the following content and hitEnter.
MiniTool Power Data Recovery canrecover deleted fileseasily within a few steps.
Thisfree file recovery softwareis user-friendly.
Even if you are new to data recovery, you’re able to master it quickly.
It can handle data recovery tasks for different types of files in various data storage devices.
This post puts forward 2 methods to get them back.
If you are interested in these methods, just try it by yourself.
But kindly be careful when working on it.