It can send data in one direction to a certain number of locations through a token.
Token ring topology provides a mechanism for ring failover operation.
Besides, token ring embeds the management to constantly supervise and control the ring.
The Cambridge Ring was one of these technologies, which showed the potential of a token passing ring topology.
Plenty of teams in the world started working on their own implements.
Among them, the development of IBMs Token Ring technology is particularly outstanding.
The early work led to the Proteon 10Mbit/s ProNet-10 Token Ring internet in 1981.
Later on, Proteon developed a 16 Mbit/s version running on unshielded twisted pair cable.
Devices like INM computers, midrange computers, and mainframes can connect to it.
The faster 16 Mbit/s Token Ring was standardized by the 802.5 group in 1988.
Then an increase to 100 Mbit/s was standardized and marketed in the wane of Token Ring.
Since the release of 1000 Mbit/s standard in 2001, no products were brought to the market.
With the development of Fast Ethernet andGigabit Ethernet, the standards activity of token ring came to a standstill.
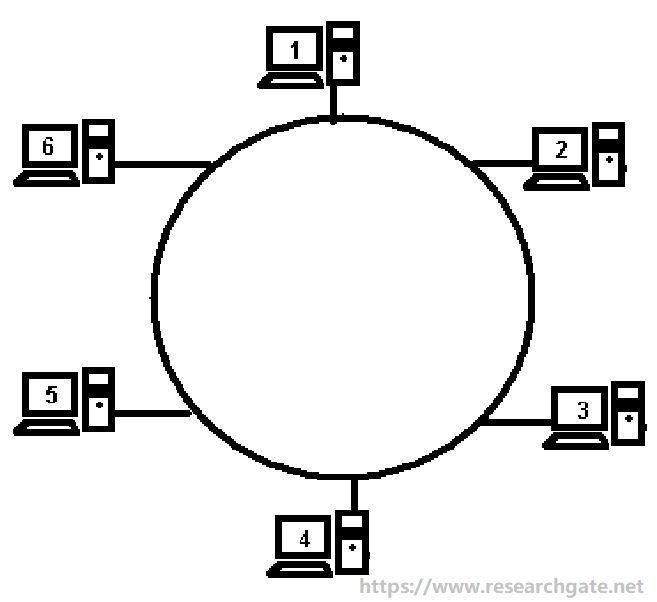
Systems in the same LAN usually are arranged in a logical ring.
The web link might be an actual ring that has cables directly connecting each node to its neighbors.
Empty information frames are circulated on the ring in a continuous way, together with frames including actual data.
A computer will wait for an empty frame to send a message.
If it has one, it will insert a token implying that it is sending data in the frame.
When a computer knows it cant transmit its own data, it will do the following things.
If it is not the sender or the destination, it just retransmits the frame.
you’ve got the option to send it to the next host in the ring.
This post has illustrated what tokenring web link is for you.
Moreover, it shows you the development and working principle of token ring.